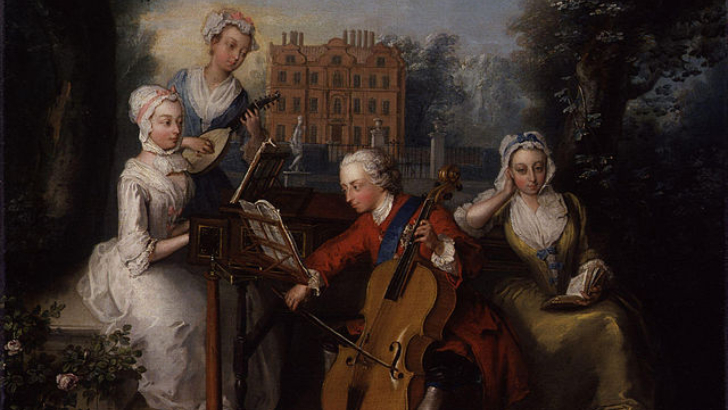This Artwork History quiz will test your understanding of historical movements and styles in art, regardless of your education level or interest in the subject. It will help you connect with your creative side and learn everything from sculpture to symbolism.
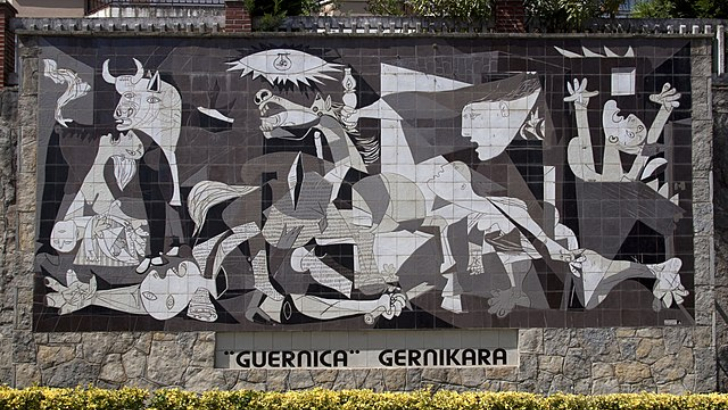
What movement did Picasso and Braque create, represented here in Picasso’s Guernica?
Cubism
One of the most important art movements of the 20th century, cubism brought avant-garde to Europe. Picasso and Braque’s Cubism involves disassembling and then reassembling objects using various abstract perspectives.
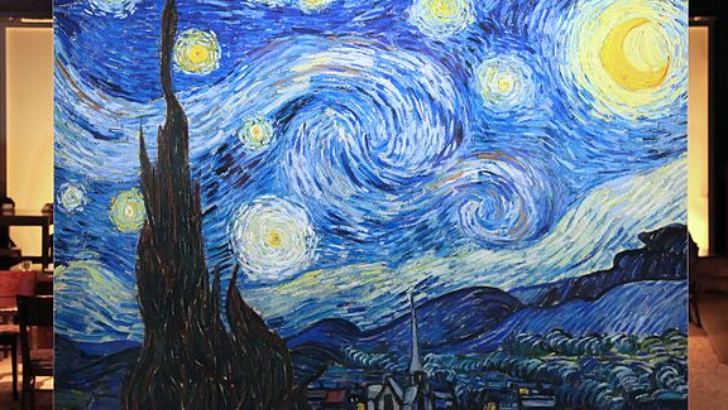
This one’s dreamy. What, specifically, is illustrated by Vincent Van Gogh’s Starry Night?
Expressionism
Van Gogh gave movement to expressionist art, which gives life to nature by using an intensified color palette and loose brushwork. The mysticism and emotion that this heavily texturized aesthetic frequently evokes.
There are lots of water lilies. What kind of artwork did Claude Monet create in the nineteenth century?
Impressionism
In the early 1860s, impressionism gained popularity as artists tried to capture the fleeting hues of sunlight. One early impressionist who excelled at this open-air attempt to capture a changing scene was Claude Monet.
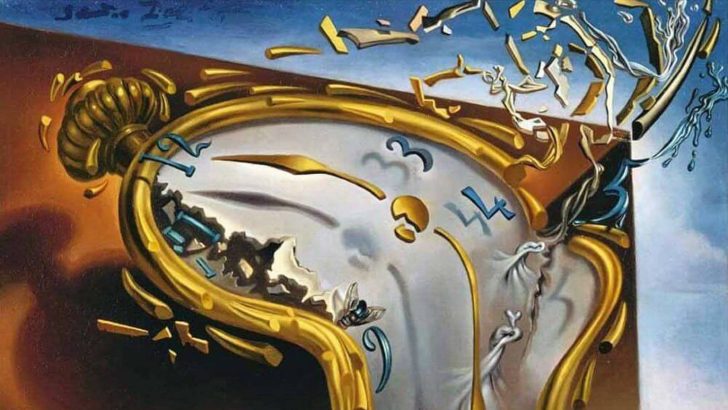
An example of this is Salvador Dali’s melting clocks.
Surrealism
Dalí, somewhat of a surrealist character, wrote the surrealist work The Persistence of Memory. This movement was created to reject reason and release the unconscious, mystical, mysterious, and magical realms that exist “beyond reality.”
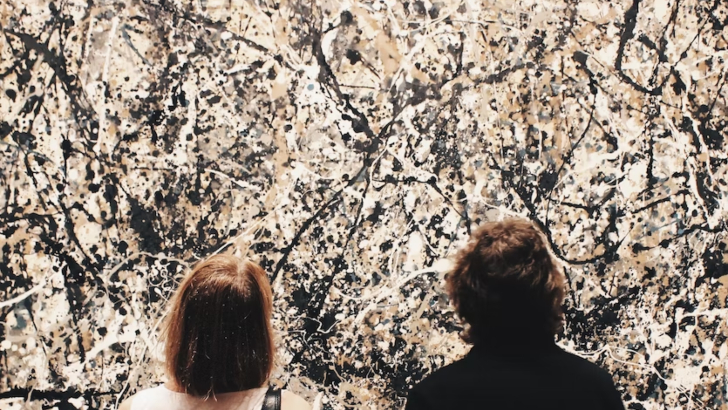
What caused Jackson Pollock to whip his paint onto the canvas?
Abstract Expressionism
The history of abstract expressionism in America began in New York City. As an interpretation of expressionism, with all the hues and feelings it stirred, abstract expressionism moved it toward the unconscious mind, as demonstrated in Pollock’s positive painting manner.
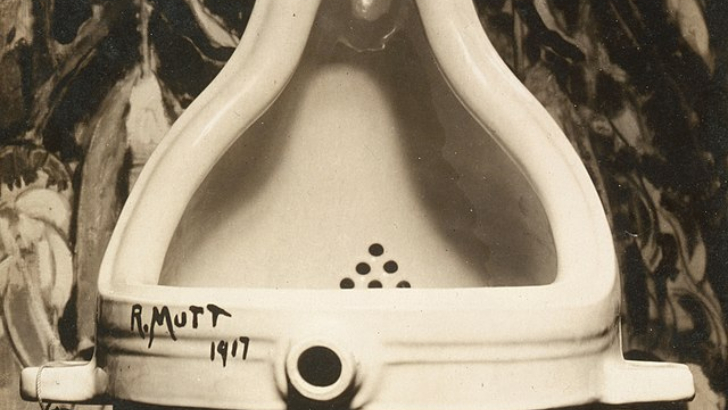
What movement did Marcel Duchamp support with his “Fountain”?
Dada
Dada wanted to destroy everything before they could create. To rebel against World War I, artists submitted works like Duchamp’s Fountain, a urinal, to the Society of Independent Artists in 1917, but it was not well received. In any case, Dada’s anti-art movement served as a prelude to surrealism.
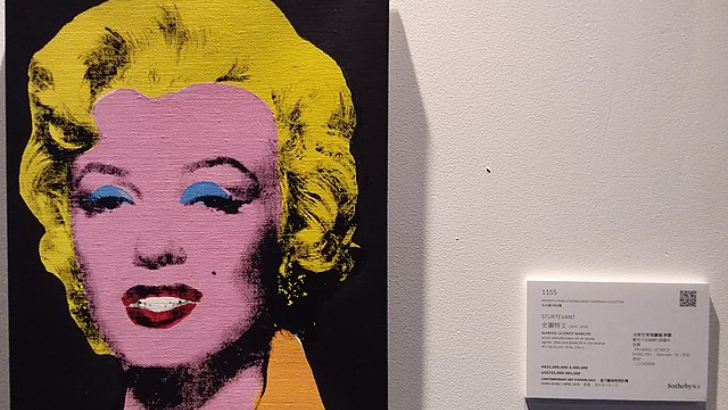
What movement was popular at the time that Andy Warhol’s Campbell’s Soup Cans and Marilyn Monroes were all the rage?
Pop Art
This commercial art was produced for a broad market. Pop art, another art-revolt movement, appeared in the 1950s by appropriating commonplace imagery from media such as movies, music, comic books, advertisements, and product packaging. Andy Warhol’s paintings and screenprints of Campbell’s Soup are one well-known example.
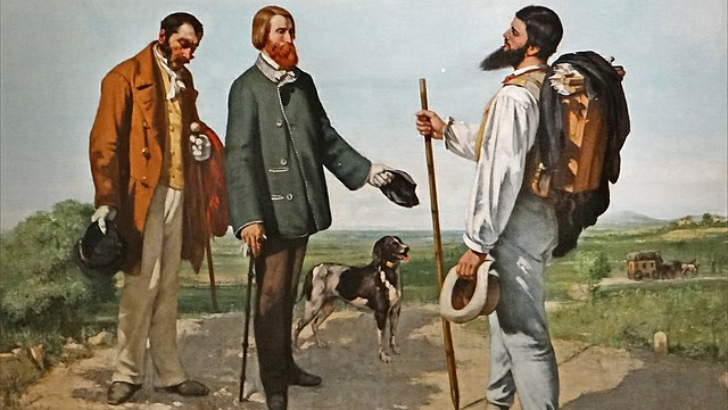
Gustave Courbet elevated this movement.
Realism
Up until the 19th century, high art occupied the spotlight. Realism and naturalism first appeared at that time. The work of Gustav Courbet is a good illustration of this. Paintings by realists frequently featured everyday scenes of the working class and reveled in grime.
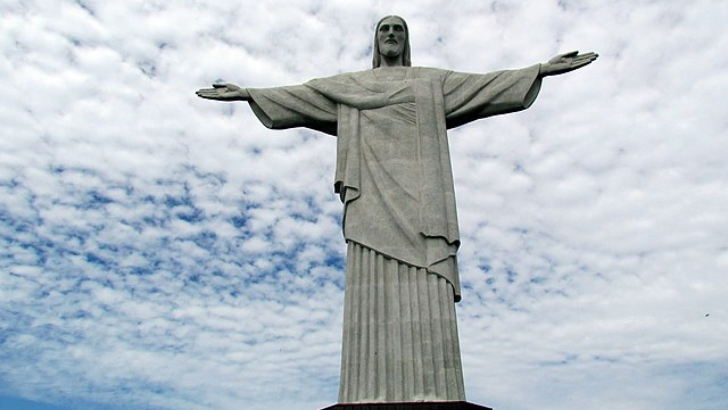
The Bauhaus School of Design inspired this movement, which is famously portrayed in Christ the Redeemer in Rio de Janeiro.
Art Deco
Similar to cubist Art Nouveau is Art Deco. The Christ, the Redeemer statue in Rio de Janeiro, created by French sculptor Paul Landowski, exhibits a much more geometric and fragmented design. The style synthesizes numerous artistic movements, drawing inspiration from modern architecture like Bauhaus designs and ancient Egyptian and Aztec art.
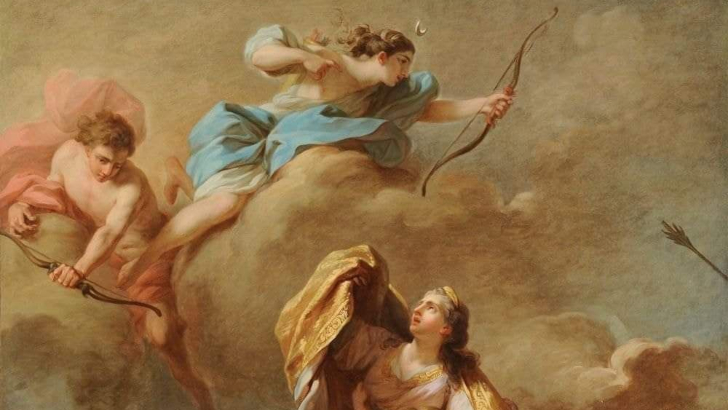
What movement is portrayed in James Barry’s artwork, such as this piece titled Apollo and Diana Attacking the Children of Niobe?
Neoclassicism
Neoclassicism emerged from the 18th-century discovery of Pompeii’s ruins, which sparked interest in classical art. Everything from sculpture to architecture to paintings, like this one by James Barry, can be seen to have been influenced by the classics.
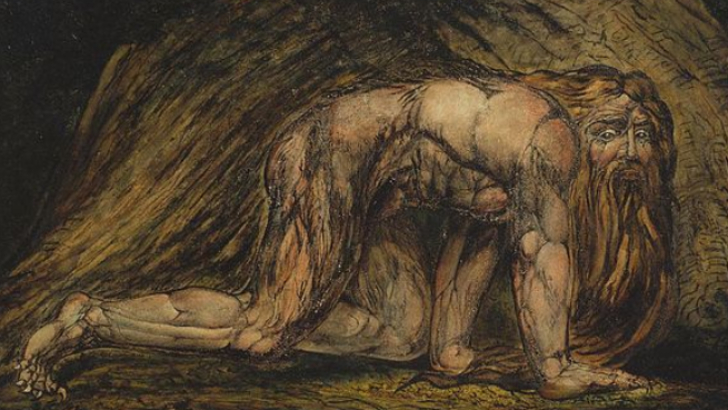
In this image of William Blake’s Nebuchadnezzar, what movement embraced emotionalism?
Romanticism
In opposition to classical restraint in the late 18th and early 19th centuries, romanticism clung to a new emotionalism. Nature, human history, and man’s relationship with God all piqued my interest.
This movement’s central idea is color, as seen in Henri Matisse’s The Red Room.
Fauvism
Fauvism is an art movement that took its name from Matisse’s paintings, which were referred to as “the wild beasts” by critics. The artworks’ sense of abstraction can be attributed to the post-impressionist movement’s wild use of paint, loose movements and forms, disregard for three-dimensional space, and vibrant, striking, and frequently complementary colors.
The Sense of Hearing by Philip Mercier has a moving movement with a seashell-inspired style.
Rococo
The Rococo style, derived from the French “rocaille” (“rock-work”), is based on the shapes of coral and seashells and uses pastels, scrolls, curves, and asymmetry to produce incredible images. Mercier and other artists’ paintings, furniture, and architecture from the 18th century exhibit decorative style.
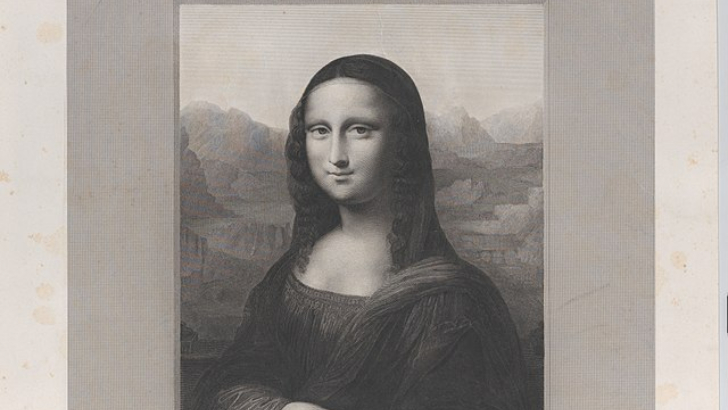
This movement was dominated by Leonardo da Vinci, Raphael, and Michelangelo, as seen in his Mona Lisa.
Renaissance
The High Renaissance, which took place in the early 16th century and was characterized by the best work of masters like Leonardo, Michelangelo, and Raphael, marked the culmination of the Renaissance of the 15th and 16th centuries. You probably already know that European art’s “rebirth” movement is one of the most well-known, with works like the Mona Lisa and the Sistine Chapel examples.
Gustav Klimt’s “Death and Life” is an example of what style?
Art Nouveau
Art Nouveau flourished in architecture and design at the beginning of the 20th century. The decorative art incorporated organic shapes, rigid geometry, and flowing lines. Just two examples of this elegant style are Death and Life and The Kiss by Gustav Klimt.
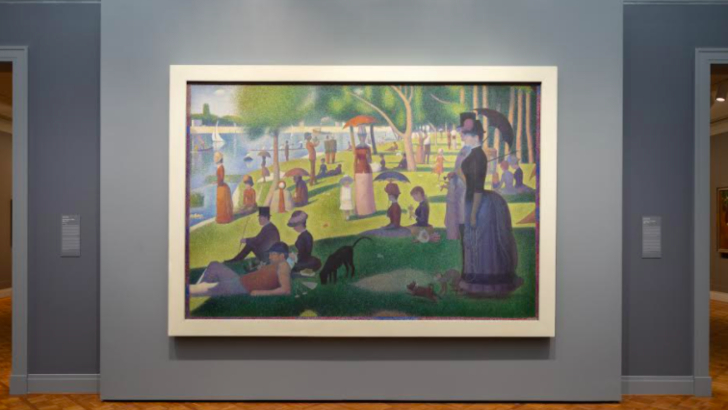
What aspects of Georges Seurat’s favorite branch of neo-impressionism can be seen in A Sunday on La Grande Jatte?
Pointillism
When viewed from a distance, pointillism uses tiny dots or strokes of color to create a chromoluminarism. This movement, which arose in the late 19th and early 20th centuries, was well-captured by Georges Seurat.
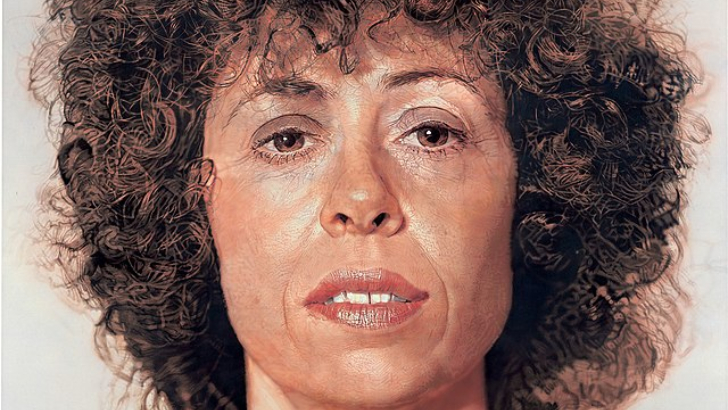
What movement is represented by Chuck Close’s incredibly detailed work?
Photorealism
This style amplified realism. Photorealism employs paint to create clear photographic-looking images, often with the simple subject matter. This latter aspect paralleled pop art.
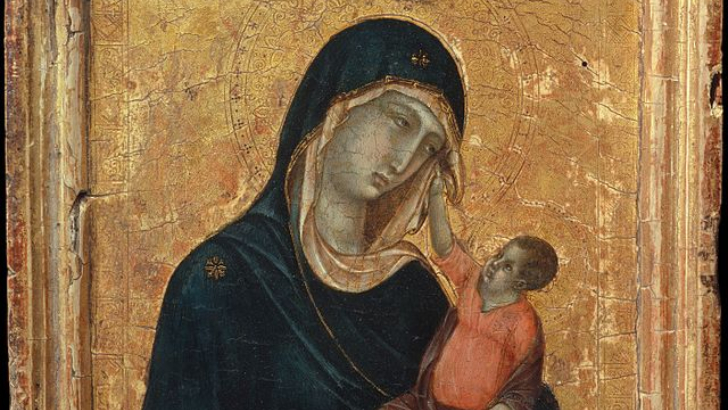
Giotto, an Italian painter, may not have dressed in black, but he devoted his life to this art style, illustrated in his Madonna and Child.
Gothic
No, goths aren’t just about dark colors and sadness. The 12th-14th century Gothic era abandoned classical ideals in favor of extraordinary manifestations in art and architecture, ranging from Notre Dame’s flying buttresses and gargoyles to stained glass windows and Gothic paintings with natural and sensual features.
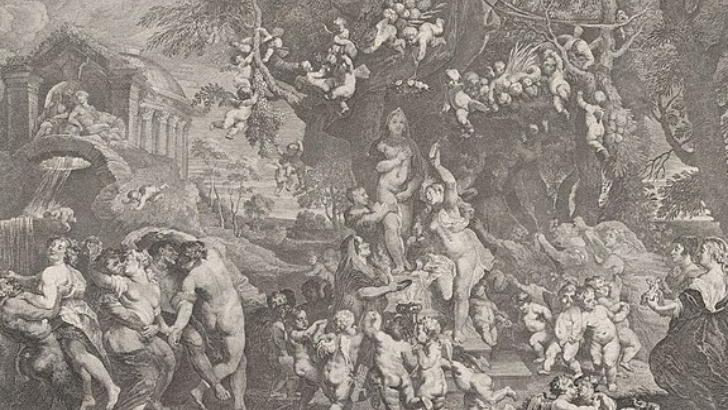
Which artistic style was promoted by Peter Paul Rubens, as seen in his work The Feast of Venus?
Baroque
The 17th-century Baroque period in Rome emphasized realism and dynamic movement in art to appeal to a reforming Catholic Church emotionally. Though it began in religious Rome, the movement spread throughout Europe, inspiring portraits, mythological subjects, and still lifes.
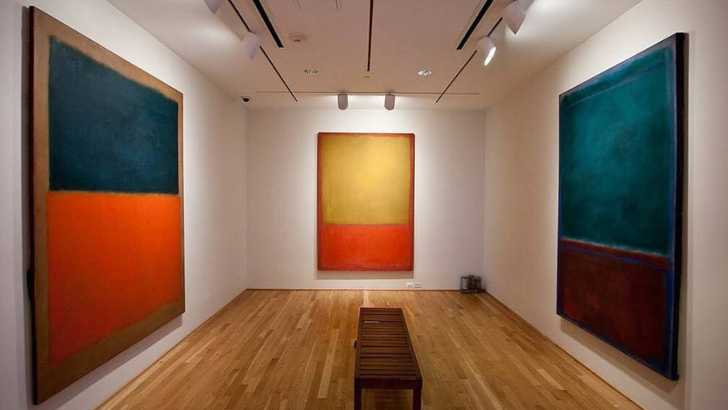
Mark Rothko was immersed in what subset of abstract expressionism?
Color Field
Color Field Painting, a subset of Abstract Expressionism, emerged in the mid-20th century with works by artists such as Mark Rothko, Clyfford Still, and Barnett Newman. The power of vibrant, expressive color was created to immerse viewers in the infinite and generate a sense of transcendence.
Sadly, you didn’t pass the quiz! 😞
Although you didn’t pass the quiz, you indeed learned a lot.
You did receive a middling score! 🤔
But the next time, you can do better.
You had no trouble with this quiz. STUPENDOUS! 🤗
You’ve just demonstrated your true genius.
[giveaway id=12098]