Put your space knowledge to the test with our fantastic 40-question quiz about the stars and galaxies.
Which of the following galaxies has lost or devoured the bulk of its interstellar matter?
Lenticular galaxies
Lenticular galaxies are disc galaxies that have lost or devoured most of their interstellar matter, leaving them with very limited star formation. They may, however, retain a significant quantity of dust in their disks. As a result, they’re mostly made up of old stars.
Which dwarf, the irregular galaxy is near to the Milky Way?
The Small Magellanic Cloud
The Small Magellanic Cloud
The Small Magellanic Cloud, also known as Nubecula Minor, is a dwarf galaxy located in close proximity to the Milky Way. The SMC is an irregular galaxy that scientists hypothesize was originally a barred spiral galaxy disturbed by the Milky Way, resulting in its uneven shape.
1998
Supernovae discoveries in 1998 provided the first visible evidence for the presence of dark energy, revealing that the universe does not expand at a constant rate, as Einstein had predicted. Rather, it accelerates its expansion.
What bright galaxy is 12 million light-years from Earth in the constellation Ursa Major?
Messier 82
The Cigar Galaxy or Messier 82, is a starburst galaxy in the constellation Ursa Major. It belongs to the M81 Group and is five times brighter than the Milky Way, with a hundred times brighter core.
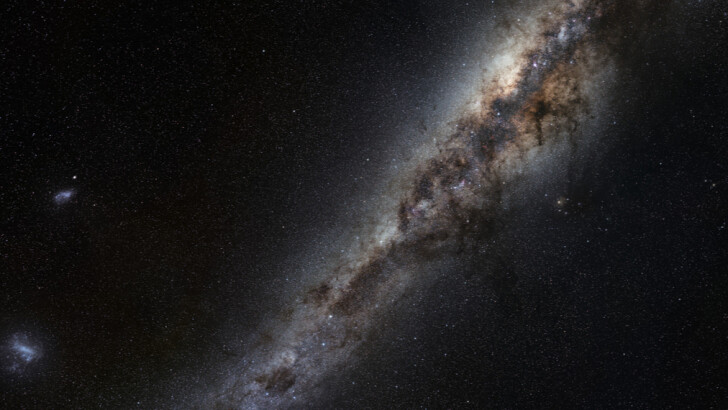
What is the name of the galaxy that encompasses our Solar System?
Milky Way
The Milky Way is the galaxy that houses our Solar System, and the name refers to how the galaxy appears in the night sky from Earth: a hazy strip of light generated by stars that are too tiny to be seen individually with the naked eye. The majority of astronomers believed that the Milky Way included all of the known stars until the early 1920s.
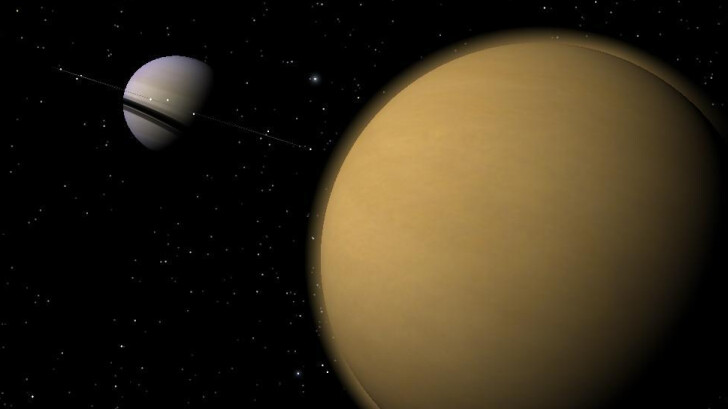
Saturn has at least 82 moons, which of the following moons is the largest?
Titan
Titan is Saturn’s biggest moon and the Solar System’s second-largest natural satellite. It is the only moon with a thick atmosphere and stable bodies at the same time. Titan is known as a planet-like moon because it is 50 percent bigger in diameter and 80 percent more massive than Earth’s moon.
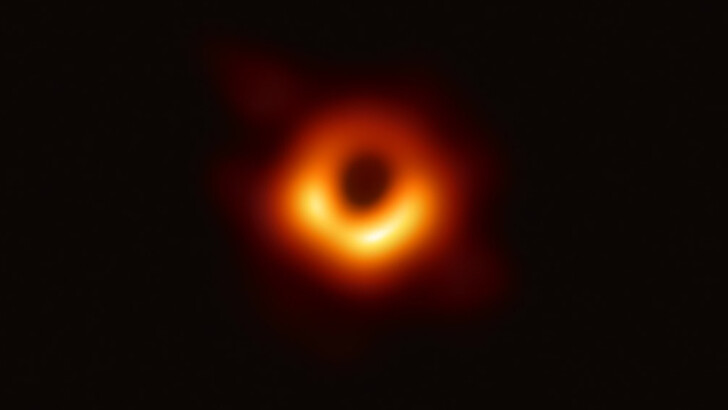
Where in the galaxy can you find the world’s first and only photographed black hole?
Messier 87
In the galaxy Messier 87, the first and only imaged black hole was discovered. The information for the image was gathered in April 2017, and the image was generated in 2018 and released on April 10, 2019. An asymmetric emission ring surrounds the black hole’s shadow in this image.
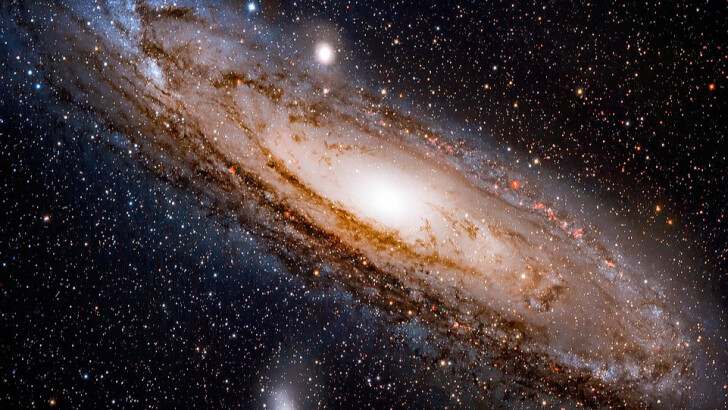
Which of these huge barred spiral galaxies is nearest to the Milky Way?
Andromeda Galaxy
The Andromeda Galaxy is approximately 2.5 million light-years from Earth. According to Greek mythology, its name comes from the constellation Andromeda, which was named after an Ethiopian princess who wedded Perseus.
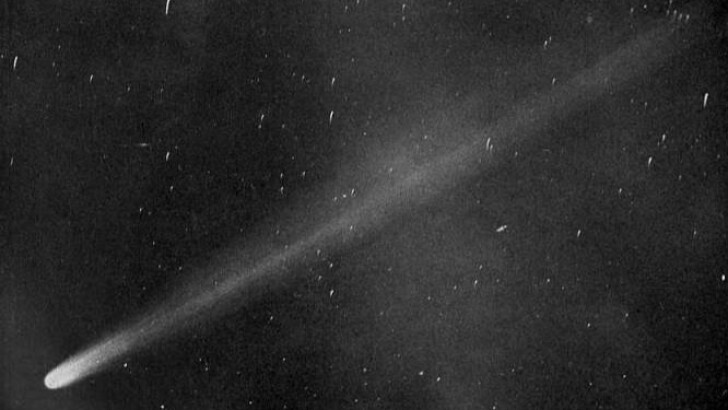
1986
Halley’s Comet is a periodic comet that comes close to Earth every 75 years, allowing a person to see it with their naked eye twice in their lifetime. It was last seen in 1986 and will be seen again in 2061.
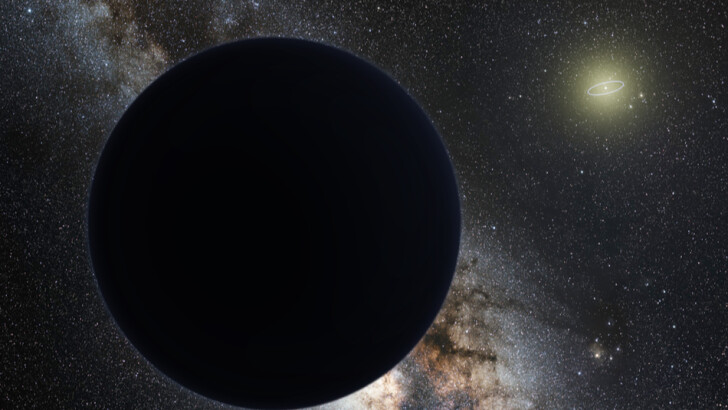
What is the name of the Solar System’s hypothetical ninth planet, which, according to two astronomers, orbits the Sun every 15,000 years?
Planet Nine
Planet Nine is a hypothetical planet in the Solar System’s farthest reaches. Its gravitational forces might explain an unlikely grouping of orbits for a collection of extreme trans-Neptunian objects, which circle the Sun beyond Neptune.
A dwarf planet is a spherical celestial body that orbits the Sun and is similar to a planet but is too small to clear its orbital region or other celestial bodies. In the Solar System, how many of these planets are there?
Five
Pluto, Eris, Ceres, Makemake, and Haumea are the five dwarf planets officially recognized by the International Astronomical Union. Several dozen more are being considered for inclusion in the group, and scientists estimate the Solar System may include hundreds, if not thousands, of dwarf planets.
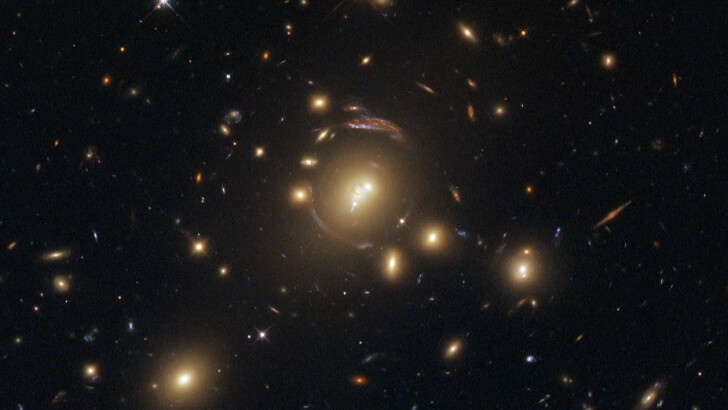
What is the name of the structure made up of hundreds to thousands of galaxies with an average mass of 10^14-10^15 suns?
Galaxy cluster
A galaxy cluster is a formation made up of hundreds to thousands of galaxies that are connected by gravity. They are among the largest known gravitationally bound structures in the universe, and until the superclusters were discovered in the 1980s, they were considered to be the largest.
Spiral
Spiral galaxies are twisted clusters of stars and gas that have beautiful shapes and are often made up of young, hot stars. Spiral galaxies have been discovered in greater numbers than elliptical and irregular galaxies.
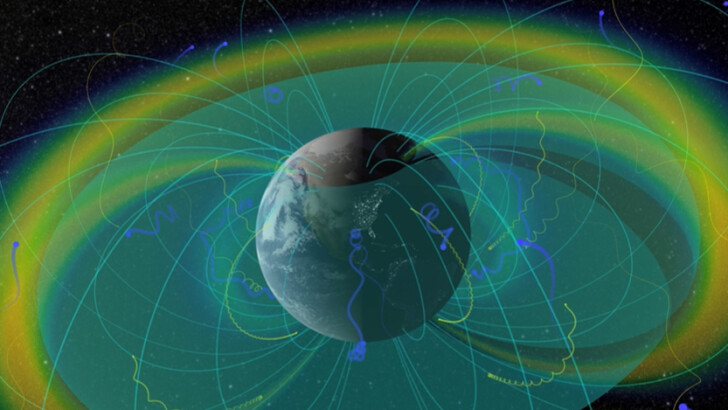
What do you name the solar wind-generated radiation belts?
Birkeland radiation belts
Van Allen radiation belts
Christofilos radiation belts
Van Allen radiation belts
The Van Allen belts are found in the inner reaches of the Earth’s magnetic fields. Highly powerful electrons and protons are trapped in them. Satellites, for example, are vulnerable to these belts and require adequate protection for their fragile components if they spend a significant amount of time there.
A light-year is a distance traveled by light in a vacuum in one Julian year, according to the International Astronomical Union. One light-year is equal to how many miles?
5.88 trillion
A light-year is a unit of measurement for astronomical distances, measuring 5.88 trillion miles (or 9.46 trillion kilometers). Because the term “light-year” includes the word “year,” it is frequently misinterpreted as a unit of time.
What is the average speed of the Milky Way galaxy as it travels through space?
600 km/s
In extragalactic frames of reference, the Milky Way as a whole move at roughly 600 kilometers per second. The Milky Way’s earliest stars, born just after the Big Bang’s Dark Ages, are almost as old as the Universe itself.
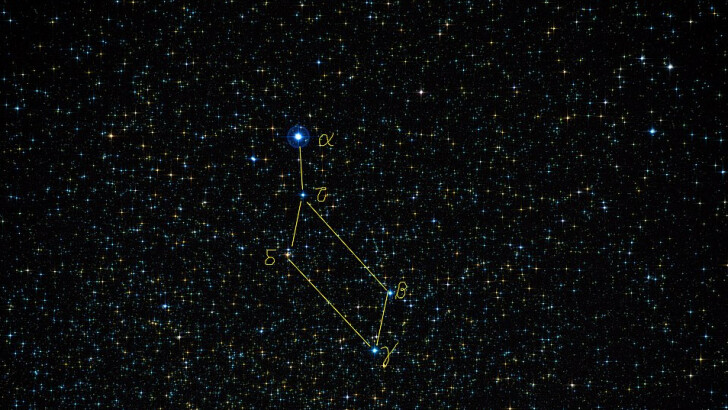
What constellation is Vega, a brilliant star only 25 light-years away from Earth?
Lyra
Vega is a brilliant star 25 light-years from Earth that may be seen in the summer sky in the Northern Hemisphere. The star lies in the constellation Lyra, and it is part of the Summer Triangle asterism, along with the stars Deneb and Altair.
Which galaxies have light masses, some merely a tenth of the mass of the Milky Way?
Irregular galaxies
Irregular galaxies have a low mass and appear prone to collisions with giant galaxies and interstellar clouds because of their small size.
With a stellar disk of 170,000-200,000 light-years in diameter, what is the second-largest galaxy in the Local Group?
Milky Way
With a star disk diameter of 170,000-200,000 light-years, our Milky Way is the second-largest galaxy in the Local Group after the Andromeda Galaxy. The Milky Way’s mass ranges from 890 billion to 1.54 trillion times that of the Sun.
Because stars do not all keep the same temperature, their hues differ. Which of these star hues is the most popular?
White
The temperature of a star determines its hue. The coldest stars are red, while the hottest are blue. The temperature of a star is determined solely by its mass. Blue stars, for example, are at least three times the size of our Sun.
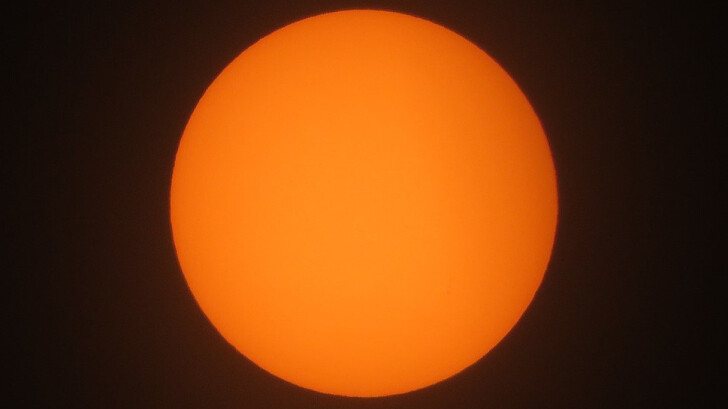
Despite being the largest object in the Solar System, the Sun is just a medium-sized star in the Milky Way galaxy. What is the classification of the Sun?
Yellow Dwarf
The Sun is classified as a yellow dwarf or a G-type main-sequence star. Although the Sun, like other G-type stars, is white, our atmosphere causes it to seem yellow when viewed from Earth.
What is the name of the spiral galaxy lying between Virgo and Corvus?
Sombrero Galaxy
The Sombrero Galaxy is 31.1 million light-years distant from the Milky Way, with a dazzling core, a huge central bulge, and a prominent dust lane visible on the edge of its outer disk. The term comes from the fact that the dust lane and bulge resemble a sombrero hat.
Name the satellite galaxy of the Milky Way that is the second or third closest to us.
The Large Magellanic Cloud
The Large Magellanic Cloud
The Large Magellanic Cloud is a Milky Way satellite galaxy. After the Sagittarius Dwarf Spheroidal Galaxy, it is either the second or third closest galaxy to ours (or possibly the Canis Major Overdensity, which has yet to be conclusively identified as a galaxy).
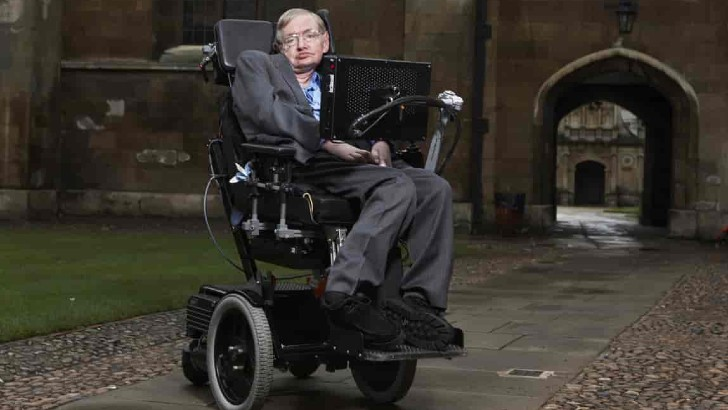
In the film The Theory of Everything, which renowned actor played the legendary astronomer Stephen Hawking?
Eddie Redmayne
The Theory of Everything is a biographical romance drama directed by James Marsh and released in 2014. It follows the life of Stephen Hawking, a theoretical physicist who is played by Eddie Redmayne.
A star’s “surface” contains mostly hydrogen and helium in a plasma state, which is typically far less dense than Earth’s air at sea level. What word would you use to describe this surface?
Photosphere
The photosphere is a star’s outer shell that emits light. The phrase comes from Ancient Greek and means “light sphere,” referring to the fact that light is thought to be produced by a spherical surface.
The isolated spiral Black Eye Galaxy, commonly known as the Sleeping Beauty Galaxy, is situated in which constellation?
Coma Berenices
The Black Eye Galaxy, also known as the Sleeping Beauty Galaxy, is an extremely isolated spiral galaxy in the northern constellation Coma Berenices, about 17 million light-years from Earth.
1992
On January 9, 1992, Aleksander Wolszczan and Dale Frail discovered two planets around the pulsar PSR 1257+12. This discovery was confirmed, and it is widely considered to be the first definitive evidence of extrasolar planets.
Which of the following stars in the constellation Ursa Minor – or the Little Dipper – is the brightest?
Polaris
Polaris, also known as Alpha Ursae Minoris, is the Earth’s present northern Pole Star or North Star, which is positioned at the point of the constellation Ursa Minor’s “handle.” Polaris is notable because it is almost perfectly aligned with the Earth’s axis. That is why, unlike the other stars, Polaris does not rise or set during the night, but rather remains in nearly the same position above the northern horizon year after year.
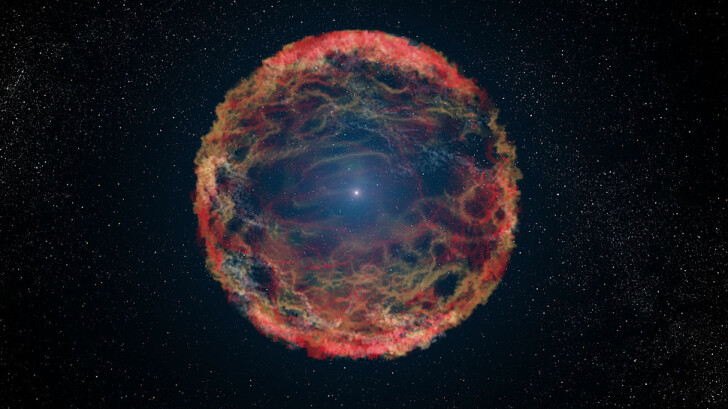
What is the name for a brilliant and powerful explosion that occurs during the last evolutionary phase of a massive star?
Supernova
A supernova is a very brilliant and intense stellar explosion that occurs during a star’s last evolutionary phases or when a white dwarf suffers uncontrolled nuclear fusion. Walter Baade and Fritz Zwicky created the word “supernova” in 1929.
When the plane of the Earth’s equator crosses the geometric center of the Sun’s disk, what happens?
Equinox
The plane of the Earth’s equator touches the geometric center of the Sun’s disk at equinoxes. On the approximate dates of March 20 and September 23, this occurs twice a year. To put it another way, it’s when the visible Sun’s center is directly above the equator.
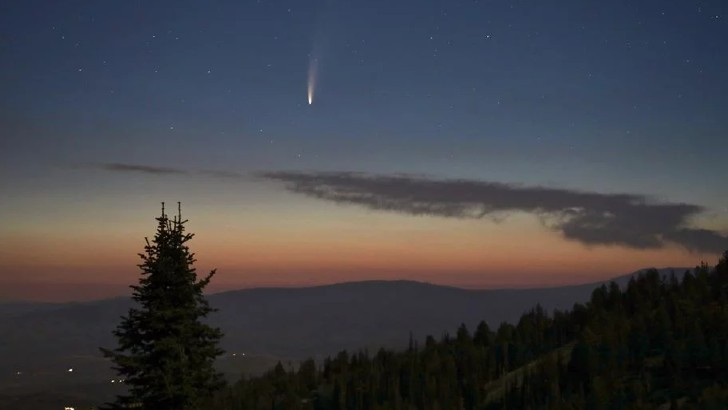
As it approaches the Sun, a frozen, tiny object in the Solar System warms up and begins to emit gases. What is it?
Comet
Comets are frozen gas, rock, and dust snowballs that circle the sun. When frozen, they are the size of a small town. When a comet approaches the Sun, however, it heats up and ejects dust and gases into a giant flaming head the size of most planets. According to astronomers, our Sun is surrounded by billions of comets.
Which planet in the Solar System is the hottest without any moons?
Venus
While Mercury is the nearest planet to the Sun, Venus has the highest surface temperature in the Solar System, at 737 degrees Fahrenheit. Venus, on the other hand, has no moons, a feature shared only by Mercury.
We learn as children that the Earth follows a nearly round path around the sun. How quickly does Earth travel this path?
200 kilometers per second
30 kilometers per second
Earth orbits at a speed of 29.78 kilometers per second (107,208 kilometers per hour; 66,616 miles per hour), fast enough to travel the length of the globe in seven minutes and the distance to the Moon in four hours.
What galaxies are made up of old, low-mass stars with little interstellar medium?
Elliptical galaxies
Many elliptical galaxies are made up of ancient, low-mass stars with limited activity. Several globular clusters round these galaxies. Approximately 10-15% of galaxies in the Virgo Supercluster are considered to be elliptical in form, despite the fact that such galaxies are uncommon in the rest of the universe.
What is the name of this Norwegian astrophysicist defined the aurorae by studying the flow of charged particles in the magnetosphere?
Knut Jørgen Røed Ødegaard
Fredrik Carl Størmer
Fredrik Carl Strmer was a Norwegian mathematician and astrophysicist who is most known for his number theory work, which includes the calculation of Pi and his theorem on consecutive smooth numbers.
If a star is massive enough to convert hydrogen atoms into helium, what phase will it enter?
Main sequence phase
A star spends the majority of its life in the main sequence phase. A star is stable at this stage because the gravitational collapse of the star is compensated by the light pressure exerted by its energy.
When it comes to space, scientists employ a wide range of methods. But how do you calculate the distance between the Earth and the Sun?
Astronomical Units
The astronomical unit is around 150 million kilometers (93 million miles) in length. It’s used to calculate the distance between the Earth and the Sun. However, because Earth round the Sun once a year, the actual distance fluctuates by about 3%.
A galaxy is a huge cloud of gas and dust containing billions of stars and their solar systems. What is it that holds everything together?
Gravity
In the cosmos, gravity is a crucial force. Gravity has an influence on the courses traveled by anything traveling through space because space objects have a gravitational pull on one another. It’s the glue that holds galaxies together and keeps planets in their orbits.
Sirius, the brightest star in the night sky, is 8.6 light-years distant from the Solar System. What is its nickname?
Dog Star
Because of its brilliance in the constellation Canis Major, Sirius is sometimes referred to as the “Dog Star.” The flooding of the Nile in Ancient Egypt and the beginning of the “dog days” for the Ancient Greeks were both predicted by Sirius’ heliacal ascension.
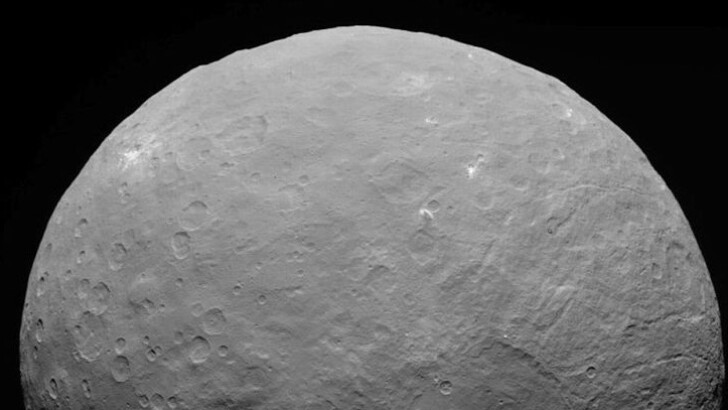
What dwarf planet lies between Mars and Jupiter in the asteroid belt and was originally assumed to be an asteroid?
Ceres
Ceres was discovered in 1801 and categorized as a planet at the time. After the finding of approximately 20 other objects with comparable paths in the 1850s, it was reduced to an asteroid. Due to its diameter of 580 miles, it was ultimately designated as a dwarf planet in 2006, making it the first asteroid large enough to be rounded by its own gravity.
Sorry, you failed. Maybe you need to read more books about our universe.
Great job. You know about the universe and you know you’re a part of it.
Watch out! We got a badass over here. Congratulations!
[giveaway id=12098]