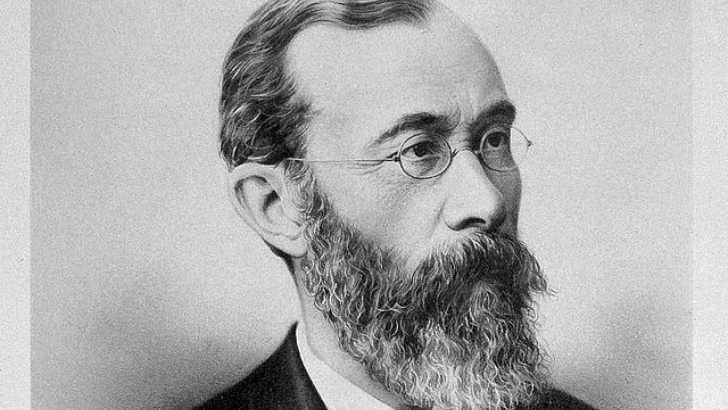The mind seeks to know how people think, act, and behave. This complex branch of science deals with conscious and unconscious phenomena and is exciting to study. Let’s take this quiz to see if you can pass Psychology 101!
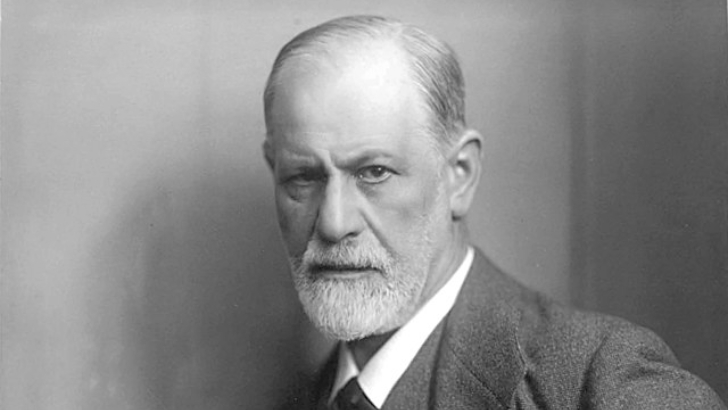
Sigmund Freud proposed a three-part structure for the human psyche: the id, ego, and _____.
Superego
According to Freud’s psychoanalytic theory of personality, the id, ego, and superego are the three fundamental components of the psyche. These three components come into play at various stages of life, and their interactions significantly impact how people behave.
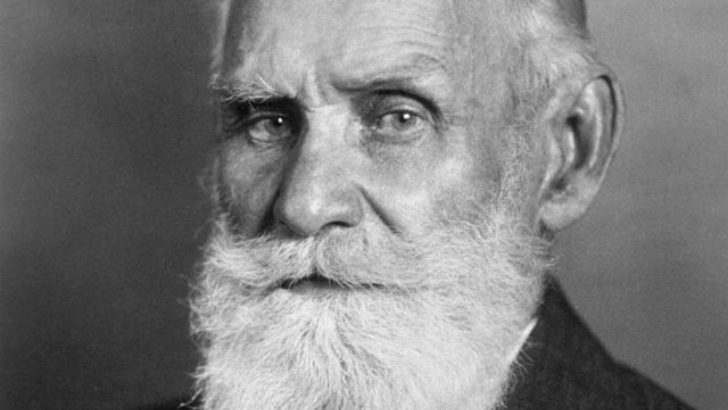
Who is a well-known Russian psychologist best known for their studies on the canine digestive system?
Ivan Pavlov
Ivan Petrovich Pavlov, a Russian physiologist, made significant contributions to the field of classical conditioning. He conducted a great deal of research on dogs’ digestive and salivary responses, which led to the theory that particular things and situations can cause a conditioned response.
What well-known branch of psychology strongly emphasizes the “how” of mental processes?
Cognitive Psychology
In cognitive psychology, the “how” of all mental operations is investigated. For instance, cognitive psychologists study how people learn and comprehend various types of information.
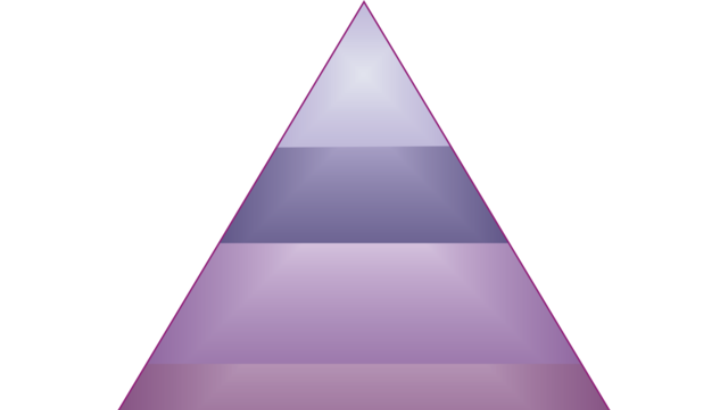
The five tiers of Abraham Maslow’s hierarchy of needs have __ at the top and physiological at the bottom.
Self-Actualization
Because higher needs do not surface until after lower needs have been met, Maslow’s hierarchy of needs is arranged in a pyramidal fashion. The top pyramid represents self-actualization, esteem, love and belonging, safety, and physiological conditions.
The word “psychology” has Greek roots that translate to “study of the psyche” or ” _____.”
Soul
The Greek word “psyche,” which means “soul,” “spirit,” or “breath,” is where the term “psychology” originates. The word’s other half comes from the Greek word “logia,” which means “study of” or “research.”
What is the psychological condition in which a person holds two or more opposing beliefs, ideas, or values?
Dissociative Identity Disorder
Cognitive Dissonance
Cognitive dissonance happens when a person has contradictory thoughts, beliefs, or attitudes. Smokers aware of the harmful effects of smoking are an excellent example of this.
The study and theories created by Swiss psychologist Jean Piaget are well-known in what field?
Childhood Development
Jean Piaget is well-known for his contributions to the field of child development, particularly his theory of cognitive development. This theory looked into how various children change intellectually as they grow up.
Two academic fields gave psychology of what initial foundation?
Anthropology and Philosophy
Philosophy and Physiology
Philosophy and Physiology
Work in the disciplines of philosophy and physiology served as the foundation for psychology. In actuality, it wasn’t until the late 1800s that psychology began to develop as a distinct academic field. William James and Wilhelm Wundt are credited with establishing psychology as a separate science from philosophy.
Which of the following is NOT one of psychology’s four main objectives?
Pacify
The four main goals of psychology are to describe, explain, predict, and control other people’s behavior and mental processes, even though it’s always a good idea to appease them.
This branch of psychology includes the profound writings of Carl Jung, Erik Erikson, and Anna Freud.
Psychoanalysis
Carl Jung, Erik Erikson, and Anna Freud contributed significantly to our understanding of psychoanalysis. This school of thought discusses how the unconscious mind affects how people behave.
How do you define metacognition?
Awareness of the thoughts of others.
A smaller, less important form of cognition.
Awareness of one’s own thought processes.
Awareness of one’s own physical body.
Awareness of one’s own thought processes.
The word “meta,” which means “beyond” or “on top of,” is the root of the concept of metacognition. Therefore, this phrase refers to one’s awareness and capacity for thought control.
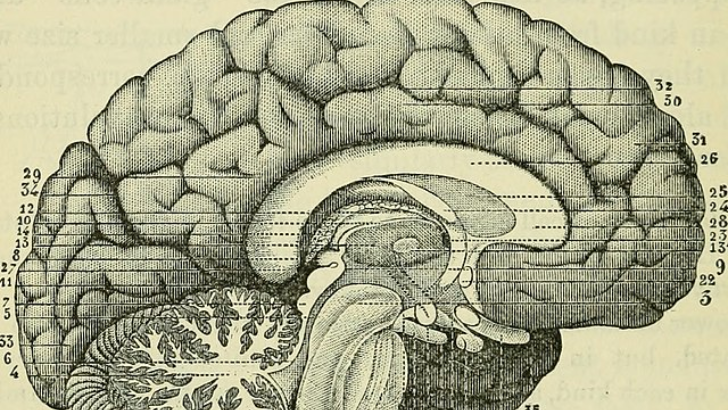
The human brain has approximately 86 billion nerve cells (AKA neurons). One of the four main components of a neuron is which of the following?
Cell Head
It is the job of neurons, which are part of the nervous system, to transmit information to other nerve cells and bodily regions. The dendrites, cell body, axon, and axon terminal are the four main components of a neuron.
Autophobia is the fear of _____, whereas acrophobia is the fear of heights.
Being Alone
The fear of being alone or lonely is known as autophobia or monophobia. Anxiety can arise for those with this phobia regardless of their location or current circumstances.
The following anxiety disorders are distinguished by unexpected and recurring bouts of what intense fear?
Generalized Anxiety Disorder
Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder
Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder
Panic Disorder
Panic disorder is characterized by unexpected and recurring irrational fear, usually accompanied by physical symptoms. These physical symptoms can range from heart palpitations and dizziness to chest and abdominal pain.
The following statements most accurately sum up classical conditioning.
A learning process where four images are repeatedly used.
A learning process where one stimuli is repeatedly studied.
A form of endurance training.
A learning process where two contrasting stimuli are repeatedly paired.
A learning process where two contrasting stimuli are repeatedly paired.
A learning process known as classical conditioning involves pairing two stimuli, one of which is biologically potent and the other previously neutral. Using this process, researchers can identify the conditioned response, also known as the learned response.
This area of the brain is in charge of hormone production, appetite regulation, and sexual behavior control.
Hypothalamus
A tiny portion of the brain, called the hypothalamus, is situated at the base, close to the pituitary gland. It regulates body temperature, upholds daily physiological cycles, manages sexual behavior, releases hormones, controls appetite, and controls emotions.
The individual’s capacity for free will is what this psychology school emphasizes most.
Humanism
In contrast to behaviorism and psychoanalysis, humanistic psychology strongly emphasizes the individual’s free will, personal development, and self-actualization.
Folk psychology’s fundamental meaning.
The study of various mental processes in humans.
The study of how people are influenced by the presence of others.
The understanding of how everyday people perceive behavior and mental states.
The study of the behavior and mental processes of non-human animals.
The understanding of how everyday people perceive behavior and mental states.
Folk psychology, also called commonsense psychology, examines how regular people, or those without a strong background in science, go about acrimoniously attributing mental states. The data gathered from ordinary people is then contrasted with viewpoints from science.
Whose influential mind is credited with founding psychology?
Wilhelm Wundt
Wilhelm Maximilian Wundt was an outstanding professor, physiologist, doctor, and philosopher. For his part in establishing psychology as a separate, independent science, he is known as the “father of psychology.”
This kind of memory involves the conscious storing and remembering of information.
Explicit Memory
Declarative memory also referred to as explicit memory, is a type of long-term memory that necessitates awareness. This type of memory, in contrast to implicit memory, involves the conscious retention and recall of information.
Unfortunately, you did not pass the quiz. 🙁
You gave your best shot but try harder next time.
Oh no, you nearly failed! 😯
You’ll almost certainly pass the next time.
Fantastic! You had no trouble with the quiz. 🤩
You’ve just revealed your intellectual mindset.
[giveaway id=12098]